How Blockchain Works: Blocks, Chains, and WeedCoin
A visual breakdown of how blockchain connects transactions into one tamper-proof system
The term “blockchain” gets tossed around a lot, but what does it really mean? The magic lies in the way blocks — groups of transactions — are linked together in a chain that grows forever. This isn’t just a clever metaphor. It’s the very structure that gives cryptocurrency its security, transparency, and unstoppable flow.
In this article, we’ll break down how blocks are created, verified, and connected to form a chain that keeps your WeedCoin (and every crypto) safe, visible, and secure without relying on banks or middlemen.
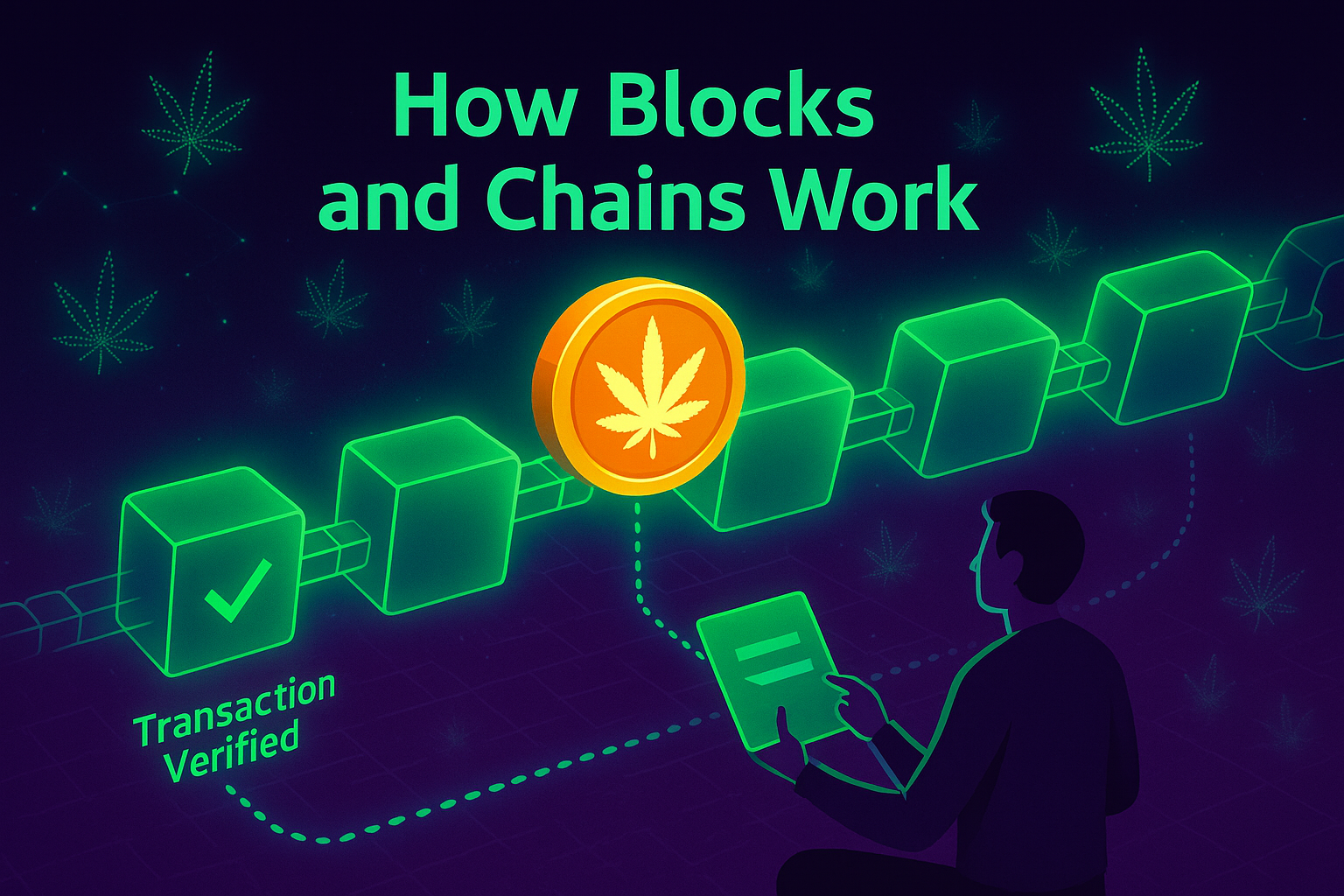
Blocks Are Batches of Transactions
Every time a crypto transaction occurs, it’s grouped with others happening at the same time. These groups are called blocks — bundles of data containing details like the sender, receiver, amount, and timestamp. Think of it like a shopping receipt, but for every transfer made across the entire network.
WeedCoin transactions are processed in the same way. When you send tokens or make a payment, your transaction becomes part of a block that’s added to the chain — permanently and publicly.
Hashing Locks It All In
Each block is given a unique cryptographic fingerprint called a hash. This hash represents the contents of the block, and even the tiniest change in the data would result in a completely different hash. It’s like a tamper-proof seal — one that instantly reveals if something’s been altered.
That’s not all. Every block also includes the hash of the block before it, creating a domino effect of security. If someone tries to mess with one block, it would change its hash — which would no longer match the next block — breaking the chain.
Chains Connect the Whole Network
The “chain” in blockchain refers to the way these blocks are linked together through their hashes. Because each one references the last, the entire history of the network becomes unchangeable. It’s not just a digital filing cabinet — it’s a living, growing timeline of every verified action.
This chaining system makes blockchain incredibly hard to hack or forge. WeedCoin builds on this same structure to guarantee that your transactions stay legit and traceable — without exposing your identity.
How Consensus Builds the Chain
Before a block is added to the chain, it must be verified by the network. This is called reaching consensus. Depending on the blockchain, this might happen through mining (proof of work) or staking (proof of stake). Once the network agrees that a block is valid, it gets added to the chain — forever.
WeedCoin operates on a chain that uses decentralized consensus to make sure your payments, tips, or token swaps are secured by the crowd — not a central authority. It’s financial democracy in action.
From Technical to Practical
While blocks and chains sound deeply technical, their purpose is simple: to create trust. They eliminate the need for banks, prevent fraud, and keep a crystal-clear record of everything that happens. That means when you use WeedCoin, you’re not just sending crypto — you’re participating in a transparent and borderless financial system.
It’s not about tech for tech’s sake. It’s about tools for freedom.
Practical Tips
- Use a blockchain explorer to view blocks and verify transactions in real time
- Hashes are like digital fingerprints — if it changes, it’s not the same block
- Understand that block time affects how fast your transaction goes through
- WeedCoin transactions are secured by the same mechanisms as major networks
- Every time you use WeedCoin, you’re adding a link to the global chain
Key Takeaways
- Blocks are groups of transactions; chains link them together securely
- Hashing protects the integrity of each block
- Every block contains a reference to the previous block
- Consensus ensures blocks are verified before joining the chain
- WeedCoin builds on this system to keep your activity transparent and secure
Trust the chain, not the bank.
WeedCoin uses this architecture to build a better way to move money, culture, and connection.













